1. A fossil fuel is the result of plant decomposition.
We all know what fossil fuel is, but how is it created? A fossil fuel is created as part of a process which involves plants from millions of years ago being broken down by microorganisms over time, a theory that dates back as far as the 1500s. The length of this process is why fossil fuels are deemed to be non-renewable resources because although they do naturally form, it takes millions of years to complete the process.
2. The Utilisation of fossil fuels paved the way for the Industrial Revolution
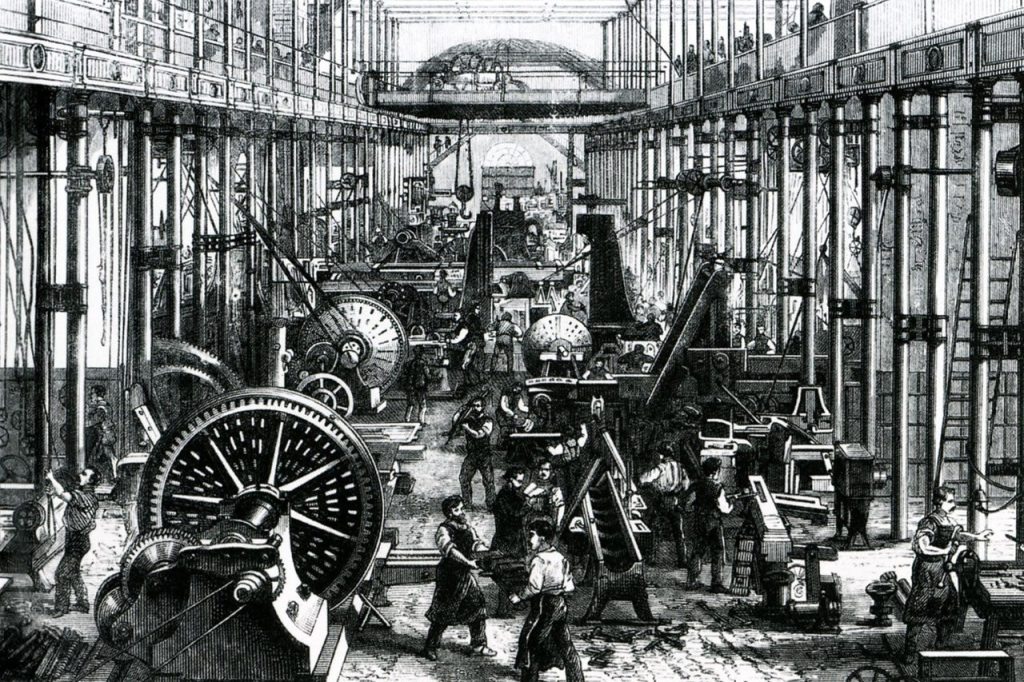
Before fossil fuels began being used on a large scale, the main source of energy for both industrial and personal use came from windmills and watermills. Early use of fossil fuels like coal and petroleum led to the invention of the internal combustion engine, something that would go on to be vital for transportation, with the increased use of vehicles, aircraft and trains.
3. Fossil fuels account for 80% of the world’s energy
Although fossil fuels used to account for up to 94% of the world’s energy usage, (which is ridiculous!) the human race is still incredibly reliant on fossil fuels with our current usage sitting at 80% which has only fluctuated slightly over the last past couple of decades. There was a significant decrease in consumption in the 1970s due to the 1970s energy crisis, where oil prices increased significantly and energy usage went from 94% to 84%.
4. Fossil fuels are made of Hydrocarbons

Hydrocarbons are organic compounds made of Hydrogen and Carbon. They are mostly found in crude oil, where they occur naturally as a result of decomposed organic matter. They are useful when it comes to providing fuel as their covalent bonds store a lot of energy, which is released when they are burned. They are not just useful for the production of fuel, other uses include plastics, medicines and cosmetics.
As you can see, Fossil fuels are incredibly interesting when you realise how much use they have in modern society. For an interesting look at the implications of the loss of certain materials, this infographic from https://www.returnloads.net/shows the knock-on effects if truckers stopped trucking.

